Self-Employment Tax Explained: Why Schedule SE Matters for Sole Proprietors
Unlike traditional employees who receive a W-2, self-employed individuals must track business expenses and deductions to determine taxable earnings. If you make estimated tax payment, self-employment taxes are included those payments, along with your estimated federal income tax payments. The Social Security to calculate the taxpayers net earnings from self-employment, 92.35% is multiplied by: portion of the tax (12.4%) only applies to the first $168,600 of your net earnings (for your 2024 tax bill). However, the Medicare portion (2.9%) applies to all earnings, with an additional 0.9% Medicare surtax for income over $200,000 (single filers) or $250,000 (married filing jointly). This additional tax is not part of your self-employment taxes—you’ll calculate and pay this with your income tax return. If you are an employee, Social Security and Medicare taxes are known as FICA taxes, and your employer pays half of your Social Security and Medicare taxes—you pay the other half through payroll deductions.
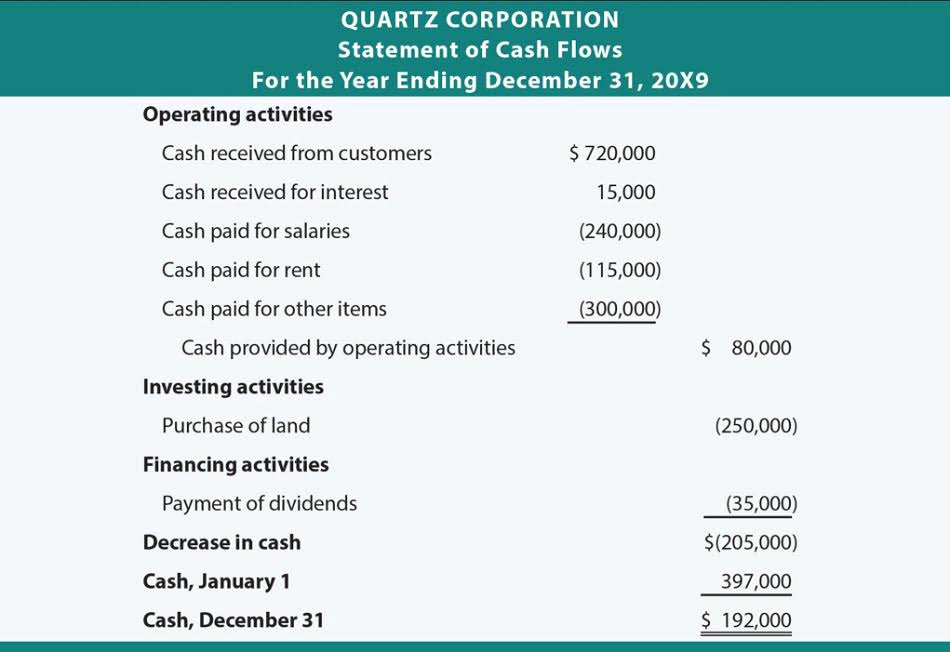
Social Security Tax and Medicare Tax

With the FICA tax on wages, the employer is incurring a 7.65% expense on each dollar paid to an employee. Medicare wages and self-employment income are combined to determine if your income exceeds the threshold. A self-employment loss should not be considered for purposes of this tax. RRTA compensation should be separately compared to the threshold. This is where you’ll add any income from being self-employed listed on your 1099 tax forms.
Per Diem Rates from the U.S. General Services Administration
- However, for tax purposes, net earnings require an additional adjustment.
- If you have $200,000 in net earnings, as in the previous example, you must pay the 2.9% Medicare tax on the entire $200,000.
- In this case, because $92,350 is the amount subject to self-employment tax, you simply multiply $92,350 by the Social Security tax rate of 12.4% to calculate your Social Security tax liability.
- The difference from regular tax software is it breaks down WHY each step happens, not just what to enter where.
- But when all is said and done, tax deductions can save you from paying the entire tax.
The tool actually does both – it explains the concepts clearly AND helps with the calculations. The difference from regular tax software is it breaks down WHY each step happens, not just what to enter where. They use AI to analyze your specific situation rather QuickBooks than generic explanations.As for whether it’s worth it compared to free IRS resources, I found it much more helpful than navigating IRS publications. The IRS documents are comprehensive but can be really difficult to understand.
- If your business expenses come out to $5,000 or less, you may be able to file Schedule C-EZ instead of Schedule C.
- The deduction is for calculating your tax base, not the rate itself.
- Necessary expenses are those that are helpful and appropriate for your business.
- Note that many members of limited liability companies (LLC) must also pay self-employment tax, as well as church employees with income over $108.28.
- The IRS documents are comprehensive but can be really difficult to understand.
Step 3: Calculate Your Social Security Tax Liability
- We’ll help you stay compliant with tax laws, maximize deductions, and make sure you’re on track for future success.
- In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know about self-employment tax in 2025 and why Schedule SE is essential for U.S. freelancers, gig workers, and small business owners.
- For example, if you earned $60,000 from freelancing but had $10,000 in business expenses, your net earnings would be $50,000.
- Self-employment tax is the combination of Social Security and Medicare taxes that self-employed individuals are responsible for paying.
- With excellence and professionalism, he has developed a solid track record in personal injury law.
You would then multiply the net $1,000 ($1,500 minus $500) by HOA Accounting 92.35% to determine your taxable earnings. In this example, only $923.50 ($1,000 multiplied by 92.35%) is subject to self-employment tax. Other situations may require you to pay self-employment tax.

File
I’ve looked into this for other countries with similar systems. To calculate your estimated tax payments, you need to estimate your net earnings for the year. You then calculate your estimated self-employment tax liability based on these earnings. This amount is then divided by four to determine each quarterly payment. However, if you expect to owe more than $1,000 in total taxes for the year, you’re also required to make quarterly estimated tax payments.

Minden vélemény számít!